The wholesale internet landscape has experienced exponential growth in recent years, opening up new avenues for businesses to streamline operations and access a broader customer base.
However, this expansion has also brought with it an increased risk of fraud, posing significant challenges for companies operating in this dynamic environment.
As the wholesale internet continues to evolve, it is crucial for businesses to understand the various fraud risks they may face and implement robust strategies to safeguard their operations.
Understanding the Wholesale Internet Landscape
The wholesale internet refers to the ecosystem of businesses that provide services, products, and infrastructure to other companies, rather than directly to end-consumers. This includes a diverse array of industries, such as web hosting, domain registration, software distribution, and e-commerce enablement, among others. The wholesale internet has become an increasingly integral part of the global business landscape, offering opportunities for increased efficiency, cost savings,
and market expansion.
However, the very nature of the wholesale internet also makes it a prime target for fraudulent activities. The anonymity and global reach of online transactions,
coupled with the complex web of intermediaries involved, create an environment ripe for exploitation by those seeking to perpetrate fraud.
Common Fraud Risks in the Wholesale Internet
- Identity Theft and Account Takeover: The wholesale internet is vulnerable to identity theft, where fraudsters obtain sensitive information,
such as login credentials or payment details, and use them to impersonate legitimate businesses.
This can lead to account takeovers, where the fraudster gains unauthorized access to an organization’s accounts and uses them to perpetrate further fraudulent activities. - Fraudulent Transactions: Wholesale internet transactions are prime targets for fraudulent activities, such as payment card fraud,
where stolen or counterfeit payment information is used to make unauthorized purchases. Fraudsters may also engage in schemes like invoice fraud,
where they submit false invoices for non-existent services or products. - Supplier and Vendor Impersonation: Fraudsters may pose as legitimate suppliers or vendors, offering attractive deals or services,
in an effort to infiltrate an organization’s supply chain. This can lead to the payment of invoices for goods or services that were never provided, or the introduction of malware or other malicious software into the organization’s systems. - Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks: Wholesale internet companies are often the targets of sophisticated phishing and social engineering attacks,
where fraudsters use deceptive tactics to manipulate employees into divulging sensitive information or facilitating unauthorized access to company resources. - Affiliate Fraud: In the wholesale internet,
many businesses rely on affiliate marketing programs to drive sales and expand their customer base.
However, these programs can be vulnerable to fraud,
such as the use of bots or fake accounts to generate fraudulent referrals or commissions. - Data Breaches and Intellectual Property Theft: The wholesale internet is a treasure trove of sensitive data, including customer information,WholeSale Internet – Fraud Risk
financial records, and proprietary business processes.
Fraudsters may attempt to gain unauthorized access to this data, either to sell it on the black market or to use it to perpetrate further fraudulent activities.
Strategies for Mitigating Fraud Risks
Navigating the fraud risks inherent in the wholesale internet requires a multi-faceted approach, with a combination of technology-based solutions,
robust internal controls,
and comprehensive employee training. By implementing these strategies, businesses can strengthen their defenses against fraud and safeguard their operations in the ever-evolving wholesale internet landscape.
- Identity Verification and Access Controls: Implementing robust identity verification procedures, such as two-factor authentication and biometric verification,
can help prevent unauthorized access to company accounts and systems.
Additionally, implementing granular access controls, and regularly reviewing and updating user permissions, can limit the potential damage caused by compromised accounts. - Fraud Detection and Monitoring: Deploying advanced fraud detection and monitoring tools can help identify and mitigate fraudulent transactions in real-time. This may include the use of machine learning algorithms to analyze transaction patterns, as well as the integration of external data sources to cross-reference suspicious activity.
- Vendor and Supplier Vetting: Conducting thorough due diligence on potential suppliers and vendors is crucial to mitigating the risk of fraudulent impersonation.
This may include verifying business licenses, checking references,
and conducting financial and credit checks to ensure the legitimacy of potential partners. - Employee Training and Awareness: Educating employees on the various fraud risks and best practices for identifying and responding to suspicious activities is essential.
This may include regular training sessions,
the development of comprehensive fraud response plans, and the promotion of a strong anti-fraud culture within the organization. - Secure Payment Processing: Implementing secure payment processing solutions,
such as end-to-end encryption and tokenization,
can help protect against payment card fraud and other financial-related fraudulent activities. Additionally, regularly reviewing and updating payment processing procedures can help ensure the ongoing effectiveness of these measures. - Cyber Security and Data Protection: Maintaining robust cyber security measures,
such as firewalls, antivirus software, and data encryption,
can help safeguard against data breaches and the theft of sensitive information. Regular vulnerability assessments and the implementation of a comprehensive data protection strategy can further strengthen an organization’s defenses. - Affiliate Program Monitoring: Closely monitoring affiliate programs for suspicious activity,
such as the use of bots or fake accounts, can help identify and mitigate instances of affiliate fraud. Implementing clear program guidelines, regular audits, and fraud detection tools can enhance the integrity of these programs. - Incident Response and Fraud Reporting: Developing and regularly updating incident response and fraud reporting procedures can help organizations quickly identify
, investigate, and respond to fraudulent activities. WholeSale Internet – Fraud Risk
This may include the establishment of dedicated fraud investigation teams, as well as the implementation of robust communication and escalation protocols.
The Evolving Landscape of Wholesale Internet Fraud
As the wholesale internet continues to evolve, so too do the tactics and techniques employed by fraudsters. Businesses operating in this dynamic environment must remain vigilant and proactive
in their approach to fraud mitigation, continuously adapting their strategies to address emerging threats.
One emerging trend in wholesale internet fraud is the
increasing sophistication of social engineering attacks. Fraudsters are becoming more adept at manipulating employees through carefully crafted phishing campaigns and other deceptive tactics,
exploiting the inherent trust and connectivity of the wholesale internet ecosystem.
Combating these threats requires a multi-pronged approach,
including comprehensive employee training, robust communication protocols, and the deployment of advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
Another area of concern is the growing prevalence of automated bot attacks,
which can be used to perpetrate a wide range of fraudulent activities,
from payment card fraud to affiliate program manipulation. Businesses must develop and implement effective bot detection and mitigation strategies,
leveraging machine learning and other advanced analytics to identify and neutralize these threats in real-time.
As the wholesale internet becomes more integrated with emerging technologies,
such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing, new fraud risks may also emerge.
Businesses must stay informed about these evolving threats and proactively address them through the continuous refinement of their fraud mitigation strategies.
Collaboration and Industry Cooperation
Effectively addressing the fraud risks in the wholesale internet landscape requires a collaborative and cooperative approach within the industry. By sharing best practices, intelligence,
and lessons learned, businesses can enhance their collective defenses and better protect the integrity of the wholesale internet ecosystem.WholeSale Internet – Fraud Risk
Industry organizations and trade associations can play a crucial role in facilitating this collaboration, providing platforms for information sharing,
the development of common standards and guidelines,
and the coordination of fraud prevention efforts.
Additionally, partnerships with law enforcement agencies and regulatory bodies can enhance the overall effectiveness of fraud mitigation strategies,
enabling the identification,
investigation, and prosecution of fraudulent activities.
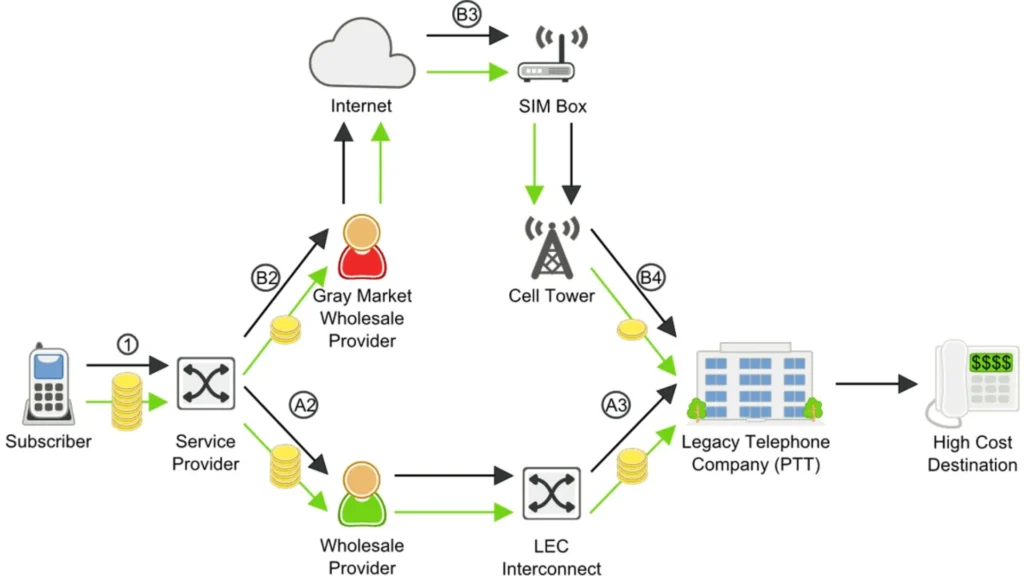
The Future of Fraud Mitigation in the Wholesale Internet
As the wholesale internet continues to evolve,
the need for robust and adaptable fraud mitigation strategies will only become more critical.
Businesses must be prepared to navigate an increasingly complex and ever-changing landscape,
leveraging the latest technologies, data analytics,
and industry collaboration to stay ahead of the curve.WholeSale Internet – Fraud Risk
The future of fraud mitigation in the wholesale internet will likely
see the increased adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms,
enabling real-time detection and response to emerging threats.
These advanced analytics tools will help businesses identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity,
allowing for proactive intervention and the prevention of losses.
Additionally,
the integration of blockchain technology and other distributed ledger systems may offer new opportunities for enhancing the transparency and traceability of wholesale internet transactions,
making it more difficult for fraudsters to perpetrate their schemes.
By harnessing the power of these emerging technologies,
businesses can strengthen their defenses and better protect their operations in the ever-evolving wholesale internet landscape.
Conclusion
The wholesale internet has become an indispensable part of the global business landscape,
offering numerous opportunities for increased efficiency, cost savings, and market expansion. However

